Overview
Neutral density (ND) filters uniformly attenuate the intensity of light over a broad spectral range. Optical Density (OD), or attenuation, is accomplished by either absorption using light absorbing glass or by a combination of absorption and reflection using a thin-film metal coating. Neutral density filters can attenuate spectral regions selected from 250 to 2500nm. OD is defined as -log10 (T) and can be specified from 0.04 to 4. Overall attenuation is additive, so ND filters can be stacked to achieve the desired OD level.
Filter Types
Absorption Glass Neutral Density (ND)
Uncoated, gray tinted glass that attenuates entirely by absorption. The degree of attention is determined by the thickness of the glass. They are not transmissive in the UV region and are generally only effective in the visible portion of the spectrum. The surface of these filters can be anti-reflected to provide the desired OD with absorbance and very low reflectance.
Metallic-Coated Neutral Density (ND)
Attenuate by a combination of reflection and absorption. This type of neutral density filter is much more uniform/neutral than the absorption glass filter and can be manufactured for a wider spectral range. (See Figure 1 for a comparison)
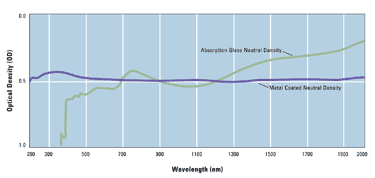
Figure 1: Neutral Density Comparison
A comparison of an absorption glass and a metal coated neutral density filter.